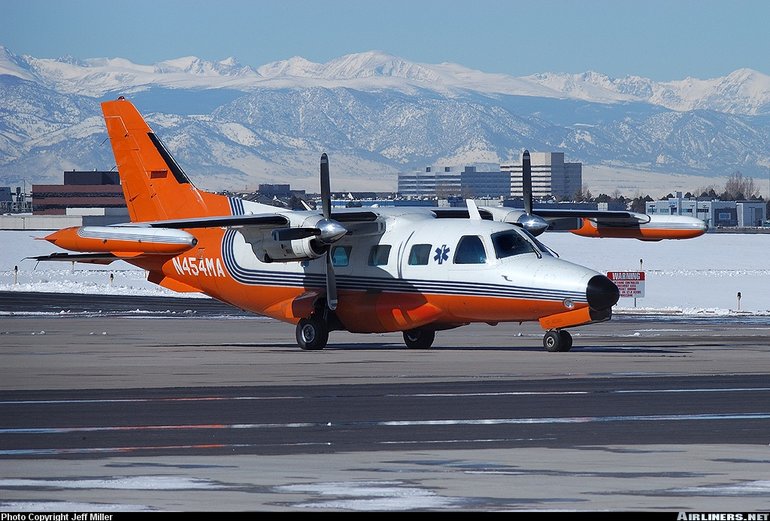
Mitsubishi MU-2
Details
Country of Origin
Japan
Type
Twin turboprop utility transport
History
The MU-2 was one of postwar Japan's most successful commercial aircraft types.
Development of the MU-2, Mitsubishi's first indigenous postwar design, began in the late 1950s. Designed as a light twin turboprop transport suitable for a variety of civil and military roles, the MU-2 first flew on September 14 1963. This first MU-2 and the handful of MU-2As built were powered by Turboméca Astazou turboprops, all other models from the MU-2B onwards had Garrett TPE331s.
The MU-2 lineup can be divided up into two basic types, the standard fuselage and stretched fuselage models. The MU-2B, E, F, K, M, P and Solitaire feature the short fuselage, the others, including the Marquise, the stretched fuselage. The first stretched fuselage MU-2G flew on January 10 1969.
The MU-2 was progressively improved and upgraded throughout its production life. Notable changes include improved and more powerful TPE331 engines, and four blade propellers from the N and P models.
Mitsubishi established a production facility for MU-2s in San Angelo, Texas in the USA in 1967 to build MU-2s for the North American and world markets. The San Angelo Mitsubishi International facility became the sole source of MU-2 production until 1986 when the line finally closed.
Mitsubishi certificated all the civil TPE331 powered MU-2s as variants of the MU-2B and they were thus given the MU-2B type number followed by a number. However, these MU-2s were also given a separate marketing designation with a sequential suffix letter. The MU-2B-10 is e.g. the MU-2D, and the MU-2B-36A is the MU-2N.
Four MU-2Cs and 16 MU-2Ks were delivered to the Japanese Army as LR-1s for the liaison and photo reconnaissance role, while 29 MU-2Es were delivered two the Japanese Air Force as search-and-rescue MU-2Ss, equipped with an extended "thimble" nose radome, increased fuel capacity, bulged observation windows, and a sliding entry door for dropping rafts.
In 2000 over 500 MU-2s were in use as corporate transports (mainly in the USA), while many have been converted as freighters.
Powerplants
MU-2B - Two 430kW (575shp) Garrett AiResearch TPE331-25A turboprops driving three blade constant speed propellers.
Marquise - Two 535kW (715shp) Garrett TPE331-10-501Ms driving four blade constant speed propellers.
Performance
MU-2B - Max cruising speed 500km/h (270kt), economical cruising speed 440km/h (237kt). Initial rate of climb 2220ft/min. Max range with reserves 1930km (1040nm).
Marquise - Max cruising speed 571km/h (308kt), economical cruising speed 547km/h (295kt). Service ceiling 29,750ft. Range with max fuel and reserves 2585km (1395nm).
Weights
MU-2B - Empty 2422kg (5340lb), max takeoff 4050kg (8930lb).
Marquise - Empty equipped 3470kg (7650lb), max takeoff 5250kg (11,575lb).
Dimensions
MU-2B - Wing span 11.94m (39ft 2in), length 10.13m (33ft 3in), height 3.94m (12ft 11in). Wing area 16.5m2 (178sq ft).
Marquise - Same except for length 12.01m (39ft 5in), height 4.17m (13ft 8in).
Capacity
Flightcrew of one or two. Short fuselage models had typical seating for seven in main cabin, longer fuselage models up to 11. Many aircraft in various corporate configurations, or used as freighters.
Production
Over 800 built. Production comprised three MU-2As, 34 MU-2Bs, four military MU-2Cs (LR-1s), 18 MU-2Ds, 16 military SAR MU-2Ss (MU-2Es), 95 MU-2Fs, 46 MU-2Gs, 108 MU-2Js, 83 MU-2Ks, 36 MU-2Ls, 27 MU-2Ms, 36 MU-2Ns, 31 MU-2Ps, 130 plus Marquise and 60 plus Solitaires.
Related Links
Mitsubishi MU-2
The backbone of this section is from the The
International Directory of Civil Aircraft by Gerard Frawley
and used with permission. To get your own copy of the book
click here.