Lockheed JetStar
Details
Country of Origin
United States of America
Type
Large size corporate jet
History
The four engined JetStar was initially designed as a private venture but was also selected to fulfil a US Air Force requirement for a multi engined light transport and crew trainer.
The first JetStar prototype first flew on September 4 1957. Two prototypes were built powered by two Bristol Siddeley Orpheus turbojets, one of these was reengined with four Pratt & Whitney JT12s in 1959 when an agreement to licence assemble the Orpheus in the United States could not be negotiated. The JT12 was selected for production aircraft, and the first of these flew in mid 1960.
The first civil configured JetStar was delivered in early 1961 and so the JetStar was the first business jet to enter service. Meanwhile the JetStar entered service with the USAF in 1962 as the C140 navaid calibration aircraft and the VC140 VIP transport in late 1961.
The turbojet powered JetStar remained in production until mid 1973, by which time development of the turbofan powered JetStar II had been announced. The JetStar II differs from the earlier aircraft primarily in its four Garrett (previously AiResearch and now AlliedSignal) TFE731 turbofans with their significantly improved fuel consumption, resulting in substantial improvements in operating costs, range and lower noise levels, while more power allows a higher maximum takeoff weight.
The first JetStar II flew on August 18 1976, with certification following in December that year. The II remained in production until 1979.
AiResearch meanwhile had already flown its own TFE731 powered conversion of the JetStar in July 1974. The first production AiResearch 731 JetStar conversion flew in March 1976.
Powerplants
JetStar - Four 14.7kN (3300lb) Pratt & Whitney JT12A6 turbojets. JetStar II - Four 16.5kN (3700lb) Garrett TFE7313 turbofans.
Performance
JetStar - Max speed 920km/h (498kt), max cruising speed 823km/h (445kt). Range with a 910kg (2000lb) payload and reserves 4585km (2476nm). JetStar II - Max cruising speed 880km/h (475kt), economical cruising speed 817km/h (440kt). Max initial rate of climb 4200ft. Service ceiling 36,000ft. Range with max fuel and reserves 5132km (2770nm), range with max payload and reserves 4818km (2600nm).
Weights
JetStar - Empty 8376kg (18,450lb), max takeoff 17,678kg (38,940lb). JetStar II - Operating empty 10,967kg (24,178lb), max takeoff 19,844kg (44,500lb).
Dimensions
JetStar & JetStar II - Wing span 16.60m (54ft 5in), length 18.42m (60ft 5in), height 6.23m (20ft 5in). Wing area 50.4m2 (542.5sq ft).
Capacity
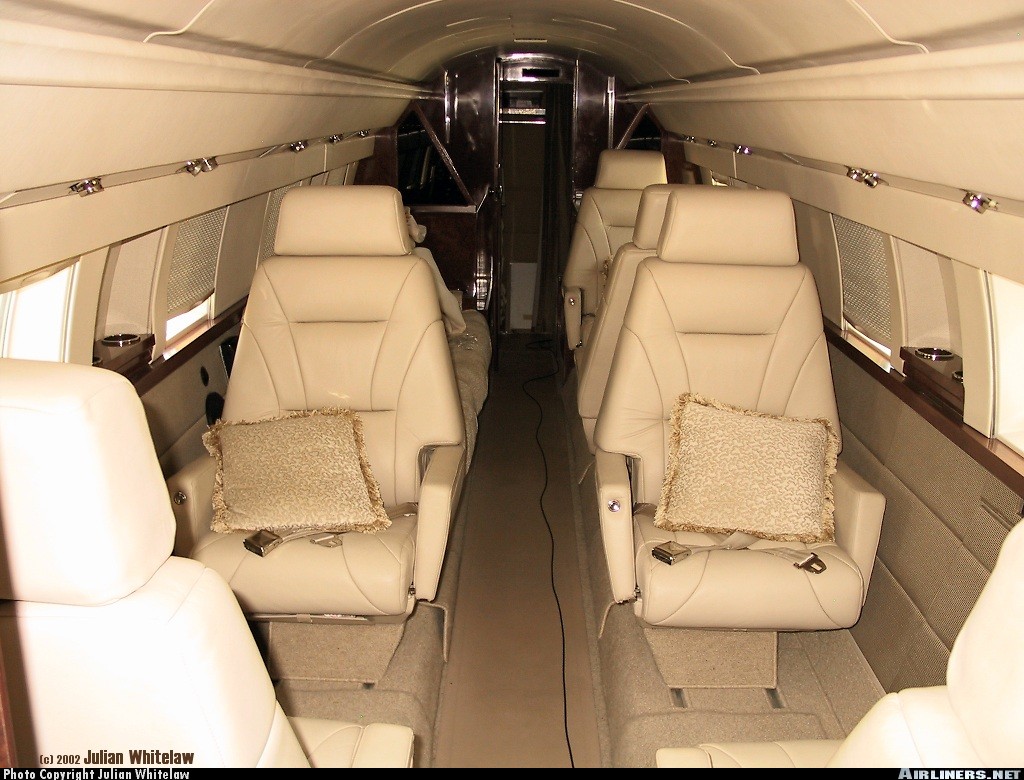
Flightcrew of two. Typical seating for eight to 10 passengers.
Production
164 turbojet powered JetStars built by mid 1973. Lockheed built 40 new build turbofan powered JetStar IIs from 1976, while Garrett converted an additional 61 to JetStar 731 configuration. Approx 29 JT12 powered JetStars, 39 JetStar IIs and 48 Garrett converted JetStars in service at late 1998.
Related Links
Lockheed JetStar
The backbone of this section is from the The
International Directory of Civil Aircraft by Gerard Frawley
and used with permission. To get your own copy of the book
click here.