Kamov Ka26 & Ka-226
Details
Country of Origin
Russia
Type
Light twin engine utility and training helicopter
History
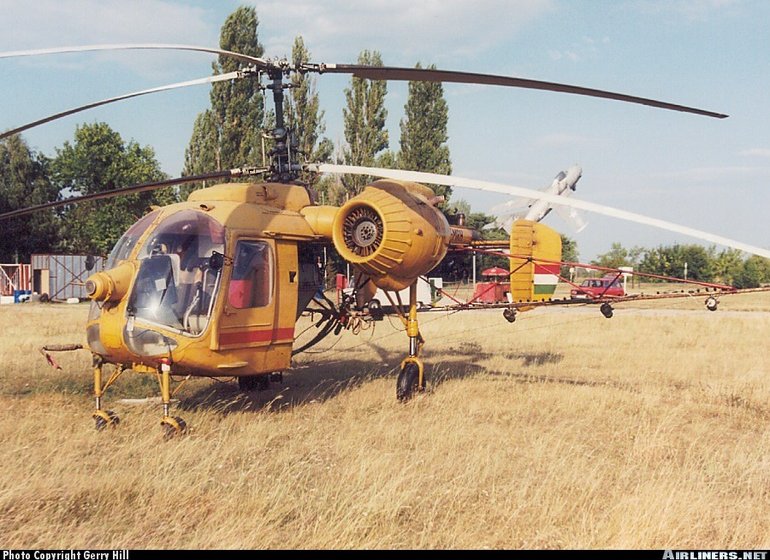
The unusually configured but useful Kamov Ka26 remains in widespread civil service in many former Soviet states.
The Ka26 (which has the NATO code name `Hoodlum') first flew in prototype form in 1965, but it did not enter service until 1970. However since then approximately 850 have been built for mainly civil service.
The uniquely configured Ka26 features two counter rotating main propellers, a Kamov characteristic that negates the need for an anti torque tail rotor. Other features include the two podded radial piston engines mounted either side of the fuselage, and the removable and exchangeable rear fuselage.
The interchangeable cabin means that the Ka26 can perform a wide variety of missions, including passenger and freight transport, air ambulance, aerial survey, and search and rescue among others with a special mission specific rear fuselage pod fitted as needed. The fuselage pod can also be removed and the aircraft instead equipped with a chemical hopper and booms for crop spraying, or it can work as an aerial crane and can also carry sling loads of freight.
The Ka26 is no longer in production, although it has been developed into the turbine powered and modernised Ka126 which first flew in 1986. Development of the Ka-126 continued into the mid 1990s but production was never undertaken.
Kamov is currently working on the improved Ka-226A. Enhancements include a new rotor system with hingless hubs and glass fibre blades, changes to the airframe including a reprofiled nose. Power is from two 335kW (450shp) Allison 250-C20R/2 turboshafts. First flight was on September 4 1997.
Powerplants
Ka-26 - Two 240kW (325hp) Vedeneyev M14V26 radial piston engines driving two counter rotating main rotors.
Performance
Ka-26 - Max level speed 170km/h (90kt), max cruising speed 150km/h (80kt), economical cruising speed 90 to 110km/h (60 to 70kt), typical agwork operating speeds 30 to 115km/h (15 to 62kt). Service ceiling 9840ft. Range with seven passengers and reserves 400km (215nm), max range with auxiliary fuel tanks 1200km (647nm). Endurance at economical cruising speed 3hr 40min.
Weights
Ka-26 - Basic aircraft operating empty 1950kg (4300lb), max takeoff 3250kg (7165lb).
Dimensions
Ka-26 - Main rotor diameter (each) 13.00m (42ft 8in), fuselage length 7.75m (25ft 5in), height 4.05m (13ft 4in). Disc area of each main rotor 132.7m2 (1430sq ft).
Capacity
Ka-26 - Seating for eight including one pilot and passenger separated from modular main cabin which seats six. For agwork can be fitted with a 900kg (1985lb) capacity hopper and spraybars in place of cabin. In air ambulance configuration can accommodate two stretchers and three seated casualties or medical attendants. For freight work it can carry a sling load or be operated with an open platform in place of the cabin module.
Production
Ka-26 - Estimated 850 built for civil and military roles, with operators in over 15 countries.
Related Links
Kamov Ka26 & Ka-226
The backbone of this section is from the The
International Directory of Civil Aircraft by Gerard Frawley
and used with permission. To get your own copy of the book
click here.